
Blog
Academia Resuscitator - written by Saba Qadri
A study by the Azim Premji University in January 2021 of over 16,000 children across five States in Classes II to VI found that 92% of children had lost at least one specific language ability from the previous year, and 82% had lost at least one mathematical ability, owing to the closure of schools due to the COVID-19. Such has been the ripple effect of this deadly tide on humanity. Apart from damaging millions of lives throughout the world, the COVID-19 pandemic confined millions of students to their homes, leading to severe losses in their studies, which according to some experts means that not only were the children pushed years behind in their learning and all-around development but also lead to increased anxiety and other mental health issues among them.
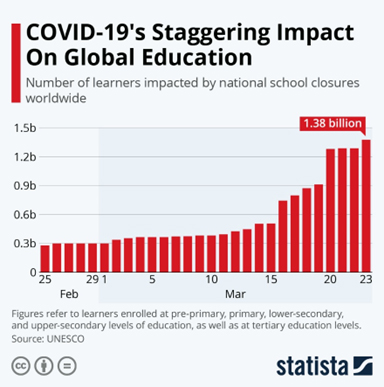
1 According to data, around 1.4 billion students were out of their pre-primary, primary, and secondary schools in more than 190 countries due to COVID-19. In India alone, the education of around 360 million students was hampered.
Between the huge disruptions and insurmountable scale of loss to children's learning, it was technology that became the glimmering ray of hope for learners around the globe. Education experts were compelled to resort to technology for the recovery of lost education. The pandemic has, nevertheless, expedited the role of technology in the education industry, favoring its digital transformation and thereby increasing its reach far more than it was prior to the pandemic.
Role of technology in the Education Industry
Apart from the severe impact of COVID-19 on human life, it greatly interrupted access to education as well. At the present outlook of the Edtech platform and freemium solutions, a report by - 2 Electronics Service Distributor RS states that 50.8% of teachers are aware of what Edtech solutions are, while 35.6% have heard about it but aren't certain about the terminology and another 13.6% has still no knowledge of the EdTech industry. However, the shutting down of educational institutions has led them to quickly evolve into a medium of learning that remains unaffected by any disaster in the unforeseen future. 3 Attempts to use computer technologies to enhance learning began with the efforts of pioneers such as Atkinson and Suppes (e.g., Atkinson, 1968; Suppes and Morningstar, 1968). Since then, Education technology as an industry is growing exponentially, valued at almost 90 billion in 2020 and rising at a projected rate of 20% year over year through 2028.
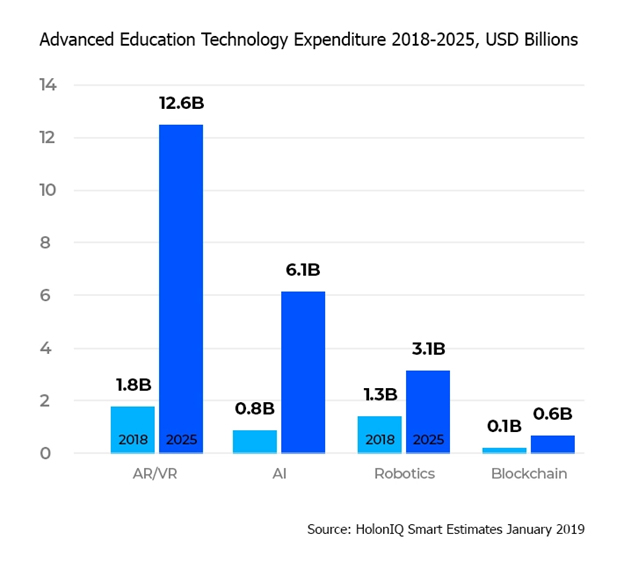
Therefore, school systems in India as well as around the globe are no longer hesitant in investing in technology and in using it to impart learning in schools while also reaching a multitude of students in their homes. They have implemented various tools of technology to facilitate learning for students.
Some of the technical tools used are:
- Classroom tablets
- Interactive projection screens
- Digital whiteboards
- Online content delivery tools
- Cloud-based learning apps
Types of Technologies Used in the Educational Institutions
A few types of technologies used in schools, colleges, and other educational institutions include:
1. Gamification - According to BlueWeave Consulting's (Washington) study, the global education gamification market will grow by at least 29% by 2027 from its current $697.26 million worth in 2020. This is owed to the aspects of the games that keep the student glued to them. When school lessons get transformed into video game-like formats, they are bound to stimulate the students' interest, leading to enhanced engagement. Improved presentation, an enticing achievement system, rewards in the form of digital badges, and a ranking system encourage the students to study and perform. These attributes of the games such as team achievements, problem-solving, earning points, etc. make learning interesting.
2. Learning Management Systems - The quality of distance learning depends on the software solutions used. Although there are many Learning Management Systems (Blackboard, Google Classroom, etc.), all of them are dedicated to helping create lessons and online courses, providing various forms of knowledge tests, communicating with teachers and other students, monitoring individual statistical parameters of each student, and many others. This technology is useful for distance learning, as well as in the classroom where computers are actively used in teaching and learning.
3. Augmented reality and virtual reality - Computer-based learning gives students a captivating experience. This is why, Augmented and Virtual reality are playing a crucial role in enhancing the understanding skills of students showing them the ancient kingdoms and their ways of life (in history classes), how the light gets reflected from a surface (in physics class) or allowing them to visit distant locations (in geography classes). The difference between Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) is primarily the fact that AR implements computer graphics in a real-world setting, while VR is an entirely virtual classroom experience.
4. Smart Class - Modernization of teaching has revolutionized classrooms. Numerous technological solutions aid teaching. These include tablets, computers, and projectors, along with software solutions that connect them all into a well-coordinated whole. Technically equipped classrooms offer well-designed multimedia lectures that enhance learning, increase student attention, offer students the freedom to learn at their individual paces, and more.
5. Robotics - Science classes of today are unimaginable without learning about robots and their role in modern society. In addition to helping students in learning to create and understand the basics of programming, robots help them to develop interpersonal skills such as teamwork, critical thinking, and time management, among others. The intricacy of subject matter related to robotics grows with the level of education, which allows for the steady development of their skills.
6. 3D printers - Creating 3D models and their printing is utilized in diverse areas of education. The advantages of this technology in education are multiple because it allows students to design various objects, from art sculptures to 3D building models. This supports their creativity through project design. 3D printers unlock various opportunities in education and different professions.
All the above forms of technology have changed the way students learn. Some of the advantages of the use of these technologies in education are:
- Enhanced communication between the teacher and learner
- Easy collaboration and Immediate evaluation
- Learning made easy through Remote Learning apps and tools
- Easy resource accessibility for better guidance
- Enhanced Interactions and inclusions in the classroom
- Simplified lessons and processes for learners
- Personalized and flexible learning
- Visual learning using videos
- 24/7 access to Learning
As per the Research Institute of America, eLearning raises retention rates from 25 to 60 percent. As more and more technology gets developed, the role of technology in the Education Industry continues to increase. At Carnation, we have a deep understanding of this rapidly growing industry that demands not only a high level of domain expertise but also a high degree of skill in technologies that are required for delivering high-quality Ed-Tech solutions. Our close association with some of the leading learning organizations and online universities of the world has allowed us to develop the unmatched domain and technical expertise that is required in this field.
If you have any comments or wish to learn more about us, you can reach us at https://www.carnationinfotech.com/
Sources
- https://www.hrw.org/report/2021/05/17/years-dont-wait-them/increased-inequalities-childrens-right-education-due-covid
- https://uk.rs-online.com/web/generalDisplay.html?id=did-you-know/the-edtech-report
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. 2000. How People Learn: Brain, Mind, Experience, and School: Expanded Edition. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. https://doi.org/10.17226/9853.